Appendix B — Git and GitHub
Introduction
You will collaborate with others and submit assignments using Git, Github, and Github Classroom. Below is a short definition for each in addition to GitHub Copilot.
- Git: a version control software typically run in the shell/terminal of your computer that helps you keep track of the history of a document (updates, changes, etc.). We’ll use a user interface, Github Desktop instead of the shell/terminal.
- Github: an online repository platform that facilitates collaboration between individuals and provides a space for you to showcase your work to others.
- Github Classroom: a system within Github that helps students to create Git/Github repositories with starter code and files provided by the instructor for assignments.
- Github Copilot: a code completion tool developed by Github and OpenAI designed to convert input English code comments to runnable code. It is trained on a selection of the English language, public Github repositories, and other publicly available source code.
Git/Github Basics
Below is a short definition for the main terms you will run into when working with Git and GitHub.
- Repository (Repo): A folder or directory that has been indicated for Git to follow changes over time.
- Add: Tell Git which changed files to add to the staging area in preparation for next commit.
- Commit: A snapshot of the current status of files and subdirectories in the Repo with a time stamp and message/description.
- Push: To communicate with collaborators, users must push their commits to the remote server, eg, Github.
- Pull: To see what your collaborators have done, users must pull any new commits from the remote server (typically Github).

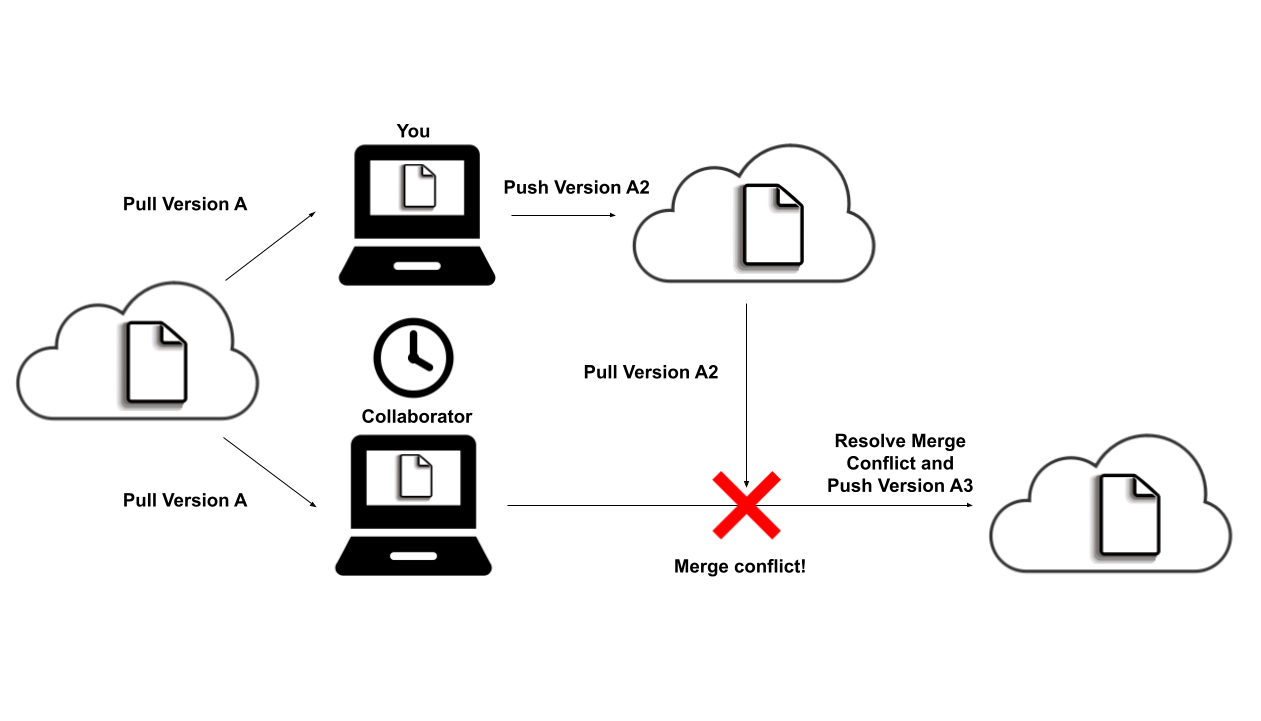
Merge Conflict
When two collaborators are working on the same committed version of the files and change the same line in a file, there will be a merge conflict. In order to proceed, the 2nd individual attempting to push a new commit will need to resolve the conflict first.
To resolve a merge conflict, follow these steps:
- Open the file(s) that have been indicated to have a conflict.
- Look for the problematic areas in the file(s). They’re surrounded by
\<\<\<\<\<\<\<and\>\>\>\>\>\>\>. The content after the first marker originates from our current working branch (HEAD). The line with seven equals signs=======separates the two conflicting changes. - Decide which code to keep then remove the
\<\<\<\<\<\<\<,\>\>\>\>\>\>\>, and=======from the file and save it. - Commit then push.